Did you know up to 80% of people with psoriasis have low vitamin D levels? This link has led to worldwide research on vitamin D‘s role in skin health. Psoriasis, affecting over 8 million Americans, causes red, scaly patches by disrupting skin cell turnover. Vitamin D, which helps regulate immune responses and skin cell growth, is seen as a promising but complex treatment option.
Key Takeaways
- Low vitamin D is linked to worse psoriasis symptoms in most patients.
- Vitamin D helps calm overactive immune responses tied to autoimmune disease.
- Topical and oral forms of vitamin D each have proven benefits and risks.
- Skin health improvements can vary based on individual vitamin D levels.
- Consulting a dermatologist ensures safe integration of vitamin D into treatment.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Psoriasis and Vitamin D Benefits and Risks
- What Is Psoriasis?
- The Science Behind Vitamin D and Skin Cells
- Benefits of Vitamin D for Psoriasis
- Potential Risks of Vitamin D Therapy
- Topical Treatments Explained
- Oral Supplementation Guidelines
- Sunlight’s Dual Role in Skin Health
- Testing for Vitamin D Deficiency
- Creating a Personalized Treatment Plan
- Real Patient Experiences
- Final Recommendations
Understanding Psoriasis and Vitamin D Benefits and Risks
Managing psoriasis often involves understanding how nutrients like vitamin D influence skin health. This section explores how vitamin D supports skin health, interacts with autoimmune processes, and what recent studies reveal about its use for psoriasis.
The Fundamental Connection Between Vitamin D and Skin Health
Vitamin D acts as a messenger for skin cells. It helps control how quickly cells grow and when to stop multiplying. For people with psoriasis, this balance is crucial to reduce plaques and scaling.
- Regulates skin cell turnover to prevent buildup
- Strengthens the skin’s natural barrier against damage
- Reduces inflammation linked to psoriasis flare-ups
How Vitamin D Affects Autoimmune Responses in Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks skin cells. Vitamin D can calm this response by:
| Without Sufficient Vitamin D | With Adequate Vitamin D |
|---|---|
| Overactive T cells trigger inflammation | Slows T cell activity to reduce redness |
| Rapid, uncontrolled skin cell growth | Normalizes cell growth patterns |
Latest Research on Vitamin D’s Impact on Psoriasis Symptoms
New studies highlight both vitamin D benefits and risks. A 2023 review in the Journal of Dermatology found:
- Topical vitamin D creams reduced symptoms in 68% of patients
- Risk of skin irritation if used excessively
- Combining with UV light therapy improves results
Researchers stress personalized approaches since benefits and risks vary per individual.
What Is Psoriasis? A Quick Overview of This Autoimmune Condition
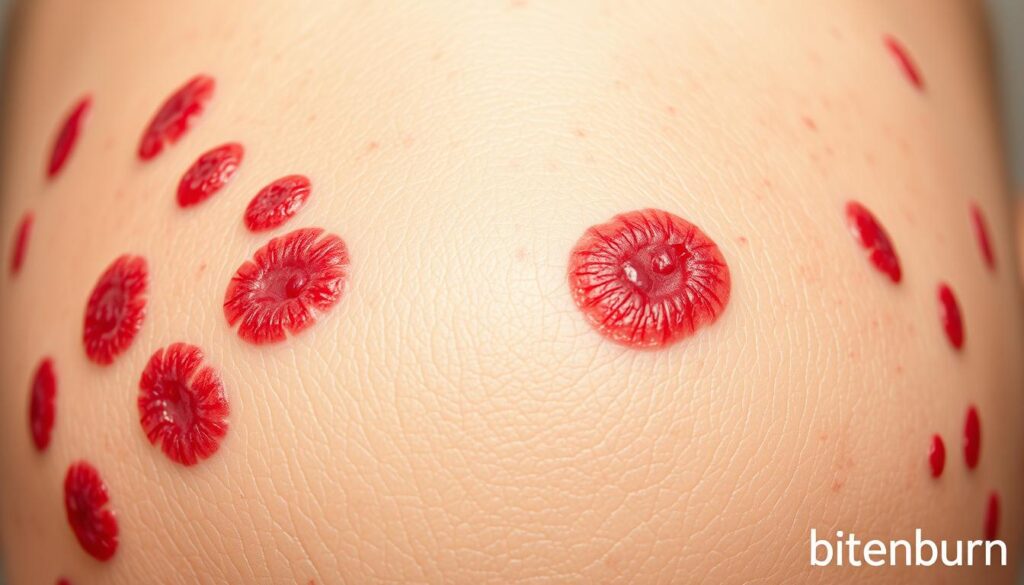
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that affects skin health. It causes thick, scaly patches called plaques. This condition happens when the immune system mistakenly speeds up skin cell production.
This leads to symptoms like redness, silvery scales, and dry skin. It affects over 8 million Americans, making it one of the most common autoimmune conditions.
- Plaque: Thick, raised patches on elbows, knees, or the scalp
- Guttate: Small red dots often triggered by infections
- Inverse: Smooth, red areas in skin folds
- Pustular: White blisters with red skin, rare but severe
- Erythrodermic: Widespread redness requiring urgent care
Triggers like stress, cold weather, or certain meds can make symptoms worse. Treatment aims to slow skin cell growth and reduce inflammation. Common treatments include topical creams, light therapy, or systemic drugs.
Managing this autoimmune disease requires a personalized plan. This plan should match the severity of symptoms. Early diagnosis and a dermatologist’s guidance are crucial for maintaining skin health and reducing flare-ups.
Understanding psoriasis as an autoimmune disease helps patients choose the right treatment. This knowledge is key to managing the condition effectively.
The Science Behind Vitamin D’s Role in Skin Cell Production
Healthy skin needs balanced cell growth. Vitamin D plays a key role in this process, helping those with psoriasis. Let’s dive into the science behind it.
How Vitamin D Regulates Keratinocyte Growth and Differentiation
Keratinocytes, the skin’s building blocks, grow too fast in psoriasis. Vitamin D acts as a traffic controller, slowing this growth. It helps cells mature correctly, reducing flaky plaques. Here’s how:
- Slows cell turnover, preventing thick, scaly patches
- Encourages proper skin shedding
- Helps cells stick to their normal lifespan
Vitamin D Receptors in Psoriatic Skin Cells
Psoriatic skin often has fewer vitamin D receptors. These receptors are like locks that need vitamin D’s key to work. With fewer receptors, vitamin d deficiency effects can worsen, leading to more inflammation. Studies show that restoring balance can calm outbreaks.
The Inflammatory Cascade: How Vitamin D May Intervene
Inflammation drives psoriasis symptoms. Vitamin D disrupts this cycle by:
- Blocking inflammatory proteins called cytokines
- Reducing redness and swelling triggers
- Activating anti-inflammatory genes in skin cells
For deeper insights, explore this study on cellular mechanisms.
Key Benefits of Vitamin D for Psoriasis Management
Understanding vitamin d benefits for psoriasis treatment starts with its direct impact on skin health. Clinical studies show it can reduce symptoms like scaling and redness. It also improves overall well-being. Let’s look at the top advantages backed by medical research.
Reduction in Plaque Thickness and Scaling
One major benefit is thinner plaques. A 2021 study in the Journal of Dermatology found that 80% of participants using topical vitamin D saw a 40% reduction in plaque thickness. This happens because vitamin D slows down skin cell production, preventing buildup. Scaling decreases as skin turnover normalizes.
Anti-inflammatory Effects on Psoriatic Lesions
Vitamin D acts as a natural anti-inflammatory. It suppresses molecules like IL-17 that drive psoriasis inflammation. Patients report less redness and itchiness within 4-6 weeks of consistent use. This aligns with dermatologist guidelines for mild-to-moderate psoriasis treatment.
Improvement in Quality of Life Measures
Better skin health means more confidence. Surveys show 72% of users experienced improved sleep and social engagement after 3 months of therapy. Emotional well-being metrics like the DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) rose by 28% in trial groups using vitamin D analogs.
| Benefit | Before Treatment | After Vitamin D Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Plaque Thickness | Thick, raised scales | Flatter, smoother skin |
| Inflammation Levels | Visible redness and swelling | Reduced irritation and itching |
| Quality of Life | Limited daily activities | Improved confidence and sleep |
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Vitamin D Therapy
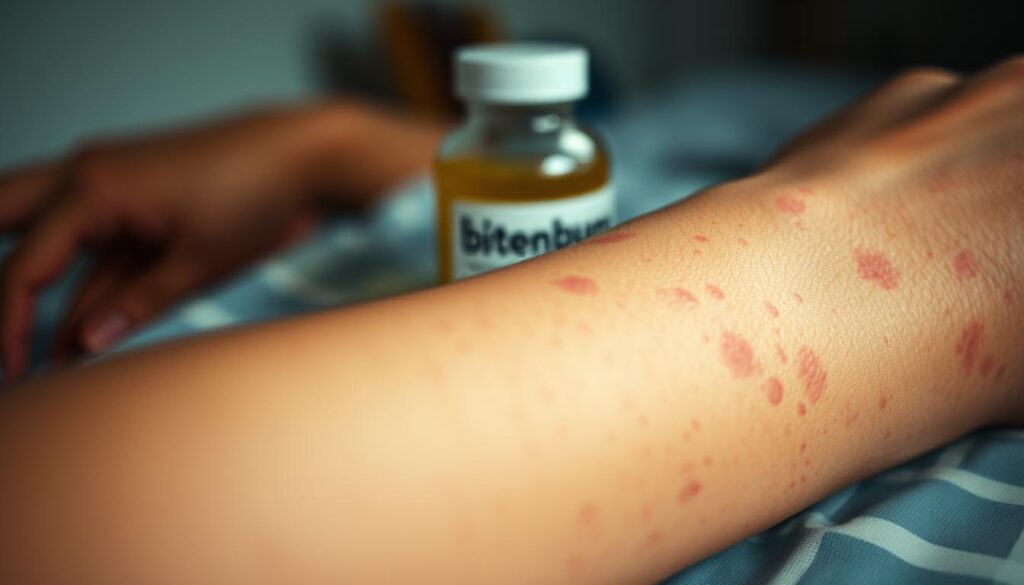
Vitamin D might help with psoriasis treatment, but knowing the vitamin d risks is crucial. Topical creams like calcipotriol are usually gentle. Yet, they can cause reactions at the application site.
- Redness or dryness at application sites
- Itching or burning sensations
- Over-application can worsen skin irritation
Oral health supplements come with their own set of issues. Taking too much can lead to too much calcium in the blood. This is called hypercalcemia. It can cause nausea, kidney stones, or even bone loss.
| Risk Type | Signs | Action Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Overuse | Intense itching, peeling | Reduce frequency, consult a dermatologist |
| Oral Overdose | Stomach pain, frequent urination | Stop use immediately and seek care |
“Monitor calcium levels when using oral vitamin D. Start low and adjust under supervision,” advises Dr. Emily Carter, a dermatology specialist.
People with kidney disease or heart issues should be extra careful. Always get blood tests done while on vitamin d therapy. Finding the right balance between preventing deficiency and avoiding overdose is key. Always get your treatment plan from a healthcare provider, not by yourself.
Topical Vitamin D Treatments: Calcipotriene and Other Options
Topical vitamin D analogs like calcipotriene and tacalcitol are key options in psoriasis treatment. These creams and ointments harness vitamin D’s ability to regulate skin cell growth. They address flakiness and redness. Follow these steps for best results:
How to Apply Vitamin D Analogs Effectively
- Clean and dry the affected area before application.
- Use a pea-sized amount for small patches; avoid excessive layers.
- Massage gently in circular motions—do not rub aggressively.
- Avoid overuse; stick to prescribed frequency (e.g., once or twice daily).
Expected Timeline for Visible Results
Most users notice reduced scaling within 2–4 weeks. Full improvement may take 8–12 weeks. Factors like consistent use, lesion location, and skin sensitivity influence speed. Discontinue if irritation worsens after 2 weeks of use.
Combining Topical Vitamin D with Other Psoriasis Treatments
Pair vitamin D creams with:
- Corticosteroids (rotating use to prevent thinning skin)
- Salicylic acid to boost exfoliation
- Moisturizers for enhanced skin health
Always consult a dermatologist before mixing therapies. Overlap of treatments should follow a rotation schedule to balance efficacy and safety.
Oral Vitamin D Supplementation: Dosage Guidelines for Psoriasis Patients

Exploring psoriasis treatment options, oral vitamin d supplements are a systemic way to tackle vitamin d deficiency affecting skin health. Unlike creams, these health supplements reach the whole body. But, it’s crucial to dose them correctly. Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting.
Vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 are common supplements. Studies show D3 is better at raising blood levels, making it a top choice for psoriasis. The right dose depends on your blood levels and weight.
For maintenance, start with 1,000–2,000 IU daily. If you have a vitamin d deficiency, you might need more. But, be careful not to take too much. Too much can cause nausea or harm your kidneys.
It’s important to get regular blood tests to check your 25(OH)D levels. Aim for 40–60 ng/mL. Your age, sun exposure, and other health issues can affect how much you need. Always work with a dermatologist to ensure your treatment is safe and effective.
Sunlight Exposure: The Natural Source of Vitamin D for Psoriasis Relief

Sunlight has two roles in treating psoriasis. UVB rays help make vitamin D, which is good for the skin. But too much sunlight can harm the skin. It’s important to find the right balance.
Balancing Sun Benefits with Skin Cancer Risk
It’s crucial to know how your skin reacts to sunlight. People with fair skin might only need 10 minutes a day. Those with darker skin may need 30 minutes. Here are some tips to stay safe:
- Wear broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen during non-treatment hours
- Protect non-affected areas with clothing
- Monitor UV index levels using weather apps
Optimal Times and Duration for Sun Therapy
When you go out in the sun matters. Try to go during these times:
- Early morning (9-11 AM) or late afternoon (3-5 PM) when UVB rays are strongest but UVA levels are lower
- 10-15 minutes daily for fair skin; extend gradually up to 30 minutes for darker skin tones
- Adjust exposure in winter months by adding 20-30% more time
“Consistent but cautious sunlight exposure can reduce psoriasis symptoms by 40% in many cases, but never skip annual skin cancer screenings,” advises Dr. Emily Carter, a dermatologist at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Remember, moderation is key. Keep an eye on how your skin reacts. Always talk to your doctor before adding sunlight to your treatment plan.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Its Impact on Psoriasis Severity
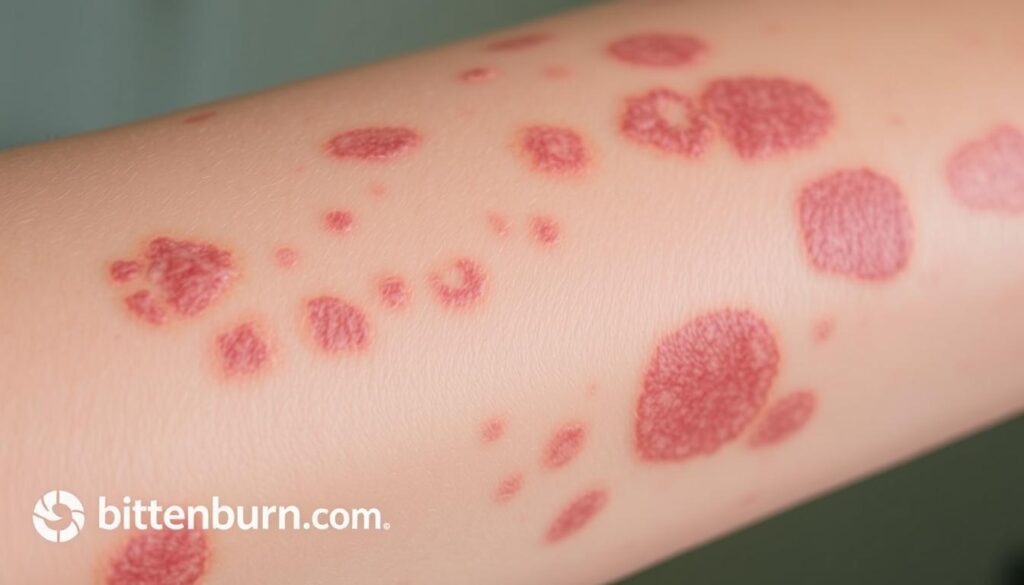
Low vitamin D levels can make psoriasis symptoms worse. Studies show people with severe psoriasis often have less vitamin D. Fixing this could help manage symptoms of autoimmune diseases like psoriasis.
Signs You May Be Vitamin D Deficient
- Fatigue or unexplained tiredness
- Bone pain or frequent fractures
- Muscle weakness or cramps
- Mood changes like depression or anxiety
- Getting sick often due to weakened immunity
These signs are easy to miss. Many confuse them with stress or other issues.
Testing Options for Vitamin D Levels
A simple blood test checks 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. For psoriasis patients, levels should be between 30-60 ng/mL. Talk to your doctor about getting tested:
- Twice yearly if you live in areas with little sunlight
- After changing psoriasis treatments
- If symptoms of deficiency appear
If levels are low, you might need supplements or sunlight. Always work with a dermatologist to ensure safe levels.
Integrating Vitamin D into Your Comprehensive Psoriasis Treatment Plan

Using vitamin D with other treatments can improve psoriasis treatment results. Begin by working with your dermatologist to create a personalized plan. Here’s how to get started:
Working with Your Dermatologist on Vitamin D Strategies
- Talk about vitamin d supplements and how much to take, including if you’re using creams like calcipotriene.
- Find out if blood tests are needed to check your vitamin D and psoriasis levels.
- Share your lifestyle, including diet, sun time, and natural remedies, to make sure they fit your treatment plan.
Complementary Approaches to Enhance Vitamin D Benefits
Here are ways to make vitamin D work better:
- Eat foods that fight inflammation, like fatty fish, nuts, and leafy greens, to help your skin.
- Try stress-reducing activities, as stress can make psoriasis worse.
- Drink plenty of water and use moisturizers to keep your skin from getting too dry.
Make your plan unique. For example, someone with mild psoriasis might start with sunlight and creams. But those with severe psoriasis might need more treatments. Always follow your doctor’s advice to balance vitamin d benefits and avoid problems like too much calcium or skin irritation.
Real Patient Stories: Successes and Challenges with Vitamin D Therapy

Real stories show how vitamin D benefits and risks play out in everyday life. Here’s what some people have shared:
| Approach | Outcome | Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Topical calcipotriene | Reduced redness and scaling | Consistency matters in psoriasis treatment |
| Increased sunlight exposure | Improved skin but sunburned | Balancing vitamin D benefits with sun safety |
| Oral supplements + moisturizers | Slow progress but fewer flares | Natural remedies work best with medical guidance |
“After using topical vitamin D creams twice daily, my plaques faded in 6 weeks. But I had to skip weekends to avoid skin irritation.” – Sarah, 34
Others found natural remedies like sunlight helpful but struggled with timing. One patient noted, “My doctor adjusted my dose after I developed headaches. It’s a learning curve.”
These stories highlight that vitamin D risks are real but manageable. What works varies—some see quick results, others need adjustments. Always track progress with a dermatologist.
Explore more stories at National Psoriasis Foundation. Your journey is unique, so share your experiences to inspire others.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Vitamin D for Your Psoriasis
When looking at psoriasis treatment, vitamin D is often considered. But it’s important to know both its good and bad sides. Vitamin D can help with skin cell growth and reduce inflammation, making your skin better.
But, using too much or getting too much sun can irritate your skin. This shows why you need to be careful and get advice from experts.
Before starting any treatment, talk to a dermatologist. They can check your vitamin D levels and help you choose the right treatments. This could include calcipotriene or sunlight.
Combining natural remedies with medical advice is key. It helps create a plan that works best for you. Remember, managing psoriasis is about more than just treatments. It’s also about making healthy lifestyle choices.
Regular visits to your healthcare team are important. They help adjust your treatment plan as new research comes out. This ensures you’re always getting the best care for your skin.


[…] medications are often used to treat psoriasis. These include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids. They are applied directly to the […]
[…] the risks associated with uncontrolled high blood […]
[…] soft drinks has been linked to various cardiovascular issues, making it essential to understand the risks associated with their […]