As Hippocrates once said, “All disease begins in the gut.” This ancient wisdom highlights the intricate link between our diet and mental wellbeing. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly found in fatty fish, play a crucial role in brain health and have been shown to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Research indicates that individuals who consume omega-3 fatty acids regularly have a lower risk of developing conditions such as heart disease, dementia, and depression. By incorporating the right foods into our diet, we can take a proactive approach to supporting our mental health.
Key Takeaways
- Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for brain health and mental wellbeing.
- Fatty fish is a rich source of omega-3s that can help alleviate anxiety and depression symptoms.
- Incorporating omega-3 rich foods into your diet can be a proactive step towards supporting mental health.
- Specific types of omega-3s (EPA, DHA, and ALA) offer different benefits for mental health.
- A balanced diet that includes omega-3 rich foods can complement traditional treatments for anxiety and depression.
Understanding Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Mental Health
The importance of omega-3 fatty acids in supporting brain function and emotional wellbeing cannot be overstated. These essential nutrients play a critical role in maintaining our mental health, and their deficiency has been linked to various mental health disorders.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are a group of polyunsaturated fats that are crucial for numerous bodily functions. There are three primary types: EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). While EPA and DHA are predominantly found in fish and seafood, ALA is derived from plant sources. Our bodies can convert ALA into EPA and DHA, though this process is not always efficient. EPA and DHA are vital for reducing inflammation and supporting brain health.
| Type of Omega-3 | Primary Sources | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| EPA | Fatty fish, fish oil supplements | Reduces inflammation |
| DHA | Fatty fish, algal oil supplements | Supports brain structure and function |
| ALA | Plant-based sources (flaxseeds, chia seeds) | Converted to EPA and DHA in the body |
The Brain-Mood Connection
The brain-mood connection is significantly influenced by omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients are incorporated into brain cell membranes, affecting neurotransmitter function and neural communication. Research has shown that omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA, impact serotonin and dopamine pathways, which are crucial for mood regulation. A deficiency in omega-3 fatty acids can lead to imbalances in these pathways, potentially contributing to anxiety and depression.
The Science Behind Omega-3s for Mental Wellbeing
Omega-3 fatty acids have been increasingly recognized for their potential in supporting mental wellbeing, backed by a growing body of scientific evidence. We will explore how these essential fatty acids influence brain function and their role in managing anxiety and depression.
How Omega-3s Affect Brain Function
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, play a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain function. EPA’s anti-inflammatory properties help reduce brain inflammation, which is associated with depression. DHA is essential for maintaining the integrity of brain cells and is a primary structural component of the brain’s grey matter, vital for memory, learning, and emotional regulation. By supporting neuroplasticity and neurogenesis, omega-3s enhance resilience against stress and mood disorders.
Research on Omega-3s for Anxiety and Depression
Extensive research has demonstrated the efficacy of omega-3 supplementation in improving mental health outcomes. Studies, including a 2019 meta-analysis, have shown that EPA-dominant omega-3 supplements are more effective than DHA at improving mood in individuals with major depressive disorder. The SMILES trial and other landmark studies have established connections between dietary omega-3 intake and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety. By examining the optimal ratios of EPA to DHA, research has highlighted their differential effects on anxiety versus depression, providing valuable insights for targeted therapeutic approaches.
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids You Need to Know
Omega-3 fatty acids are not created equal; there are three main types that support mental health in distinct ways. Understanding these differences is key to harnessing their benefits.
EPA: The Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouse
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) is known for its potent anti-inflammatory properties, which are particularly effective in reducing symptoms of depression. By lowering chronic inflammation, EPA supports brain health and can help alleviate mood disorders.
DHA: Essential for Brain Structure
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is crucial for maintaining the structure of brain cells, particularly in areas responsible for emotional processing and stress response. Without sufficient DHA, the brain’s ability to communicate and process information can be compromised.
ALA: The Plant-Based Precursor
ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) is a plant-based omega-3 precursor that the body converts into EPA and DHA. However, this conversion process is often inefficient in humans, making direct consumption of EPA and DHA important for optimal mental health benefits.
Top Omega-3 Rich Foods for Anxiety and Depression
Boosting your mental wellbeing starts with the right foods, particularly those rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 rich foods can play a significant role in alleviating symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Fatty Fish Sources
Fatty fish are among the richest sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, which are crucial for brain function and mental health.
Wild-Caught Salmon
Wild-caught salmon is an excellent choice, offering approximately 4 grams of omega-3s per 3.5-ounce serving. Its optimal EPA:DHA ratio makes it particularly beneficial for mental health.
Mackerel
Mackerel is another fatty fish that stands out for its high omega-3 content, providing 4-5 grams per 3.5-ounce serving. It’s one of the most potent natural sources of these beneficial fatty acids.
Sardines
Sardines are small, oily fish that are rich in omega-3s, with about 2 grams per 3.5-ounce serving. They are not only nutritious but also more sustainable and affordable than larger fish.
Anchovies
Anchovies are another small fish that pack a nutritional punch, offering about 1 gram of omega-3s per 3.5-ounce serving. They are often used in various dishes and can be a convenient way to boost omega-3 intake.
Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources
For those following a plant-based diet, there are several options rich in ALA, a type of omega-3 fatty acid.
Flaxseeds
Flaxseeds are a potent source of ALA, with ground flaxseed offering about 2 grams per tablespoon. It’s essential to consume them ground to maximize bioavailability.
Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are another excellent plant-based source, providing about 5 grams of ALA per ounce. They are versatile and can be easily incorporated into various meals.
Walnuts
Walnuts are a nutritious snack rich in ALA, offering about 2.5 grams per ounce. They are a convenient way to support mental health through diet.
Soybeans
Soybeans, particularly when dry-roasted, can provide a good amount of ALA, with about 0.5 grams per half cup. They are a valuable option for those looking for plant-based omega-3 sources.
Other Notable Sources
Beyond fatty fish and plant-based sources, there are other foods that can contribute to your omega-3 intake.
Oysters
Oysters are a less common but valuable source, offering about 0.5 grams of omega-3s per 3.5-ounce serving. They are also rich in other nutrients beneficial for mental health.
Algal Oil
Algal oil is a vegan-friendly source of direct EPA and DHA, making it an excellent option for vegetarians and vegans. It’s available in supplement form and can be a convenient way to ensure adequate omega-3 intake.
Hemp Seeds
Hemp seeds are another nutritious option, though their omega-3 content is generally lower compared to other sources. They still offer a good nutritional profile and can be part of a balanced diet.
Optimal Omega-3 Intake for Mental Health Benefits

Understanding the optimal intake of omega-3 fatty acids is crucial for maximizing their mental health benefits. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, play a significant role in brain function and mood regulation. The ideal intake varies based on factors such as age, health status, and diet.
Recommended Daily Dosages
The World Health Organization recommends consuming 0.25 to 2 grams of combined EPA and DHA per day, which can be achieved by eating two servings of fatty fish per week. For plant-based omega-3 sources, the National Institutes of Health suggests an adequate intake of 1,100 to 1,600 mg of ALA per day. A 3:2 ratio of EPA to DHA has been found to yield optimal mental health benefits.
Balancing Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Maintaining a balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids is essential for overall health. Modern diets often have an imbalanced ratio, typically around 20:1 (omega-6 to omega-3), which can contribute to inflammation and mood disorders. Achieving a more ideal ratio of 4:1 can be done through dietary adjustments, such as increasing consumption of omega-3 rich foods and reducing intake of omega-6 rich foods.
Incorporating Omega-3 Rich Foods Into Your Diet

A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids is a vital component of maintaining good mental health and reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. We recommend making conscious dietary choices to include more omega-3 rich foods.
Simple Dietary Swaps
Simple dietary swaps can significantly boost your omega-3 intake. Replace conventional eggs with omega-3 enriched eggs, use flaxseed oil instead of vegetable oil, and opt for wild-caught fish over farm-raised options. These swaps are easy to make and can have a substantial impact on your overall omega-3 consumption.
Meal Planning Tips
Effective meal planning is key to ensuring adequate omega-3 intake. Include a variety of omega-3 rich foods in your meals, such as fatty fish for dinner, walnuts or chia seeds for snacks, and flaxseeds in your breakfast oatmeal or smoothie. Planning your meals around these foods helps maintain consistency, which is crucial for experiencing the mental health benefits of omega-3s.
Storage and Preparation to Preserve Omega-3s
Proper storage and preparation of omega-3 rich foods are essential to preserving their nutritional value. Omega-3 fatty acids are sensitive to heat, light, and air, so it’s crucial to store them in a cool, dark place and cook them using methods that minimize exposure to high temperatures. By doing so, you can ensure that you’re getting the most out of your omega-3 rich foods.
Omega-3 Supplements: When and How to Use Them

Omega-3 supplements can be a valuable addition to your mental health regimen, but choosing the right one is crucial. When supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids, it’s essential to focus on the balance between EPA and DHA. A 3:2 ratio of EPA to DHA has been found to yield optimal mental health benefits, particularly in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Fish Oil vs. Algal Oil
Most omega-3 supplements are derived from fish oil, which is high in both EPA and DHA, making it an excellent option for those seeking a potent source of omega-3s. For vegans or vegetarians, algal oil is a great alternative as it’s the only plant-based source containing DHA and EPA.
What to Look for in Quality Supplements
When choosing an omega-3 supplement, look for products that are third-party tested for purity to ensure they are free from heavy metals and contaminants. Also, consider the form of the supplement, such as triglyceride or ethyl ester, and check for freshness indicators.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While omega-3 supplements are generally safe, potential side effects include “fishy burps” and interactions with certain medications. To minimize digestive discomfort, gradually introduce supplements into your regimen.
By understanding the different types of omega-3 supplements and what to look for in quality products, you can make an informed decision to support your mental health.
Delicious Omega-3 Rich Recipes
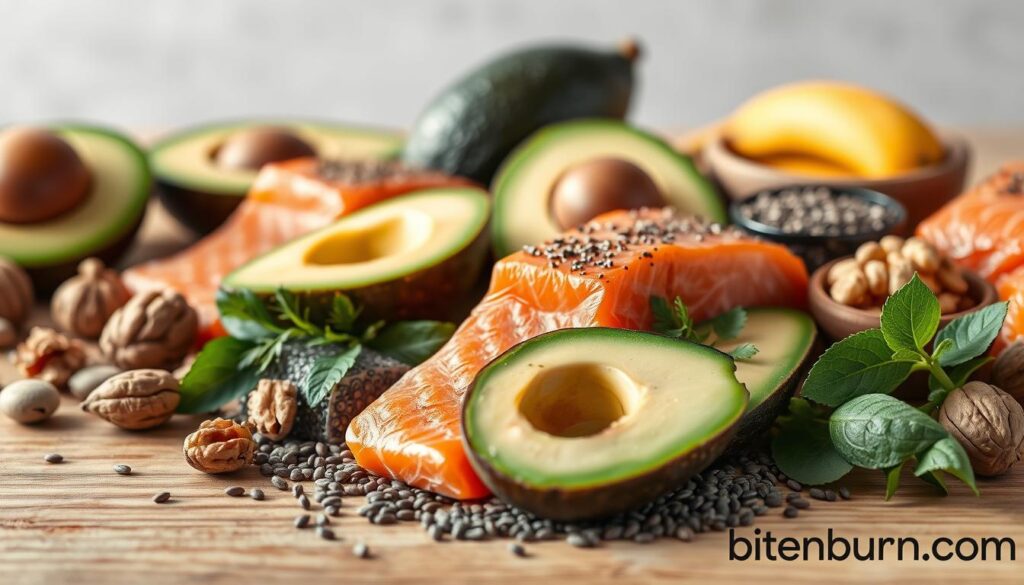

Incorporating omega-3 rich foods into your diet can be both delicious and beneficial for mental health. Here are three simple recipes to boost your omega-3 intake.
Grilled Wild-Caught Salmon with Lemon Herb Quinoa
This recipe delivers approximately 4 grams of omega-3 fatty acids per serving. To make it, you’ll need 2 wild-caught salmon fillets, 1 cup cooked quinoa, 1 tablespoon olive oil, 2 tablespoons lemon juice, and fresh parsley or dill. Grill the salmon for 5-7 minutes per side and serve with quinoa tossed with fresh herbs.
Walnut and Chia Seed Breakfast Bowl
This breakfast bowl combines walnuts and chia seeds for a boost of ALA omega-3s. Mix 1/2 cup chia seeds with almond milk, then top with 1/4 cup chopped walnuts and fresh fruit. This recipe is rich in fiber and healthy fats to keep you full.
Sardine and Avocado Toast
For a quick and budget-friendly option, try sardine and avocado toast. Top whole-grain toast with mashed avocado, 2 sardines, and a squeeze of lemon juice. This recipe provides approximately 2 grams of omega-3s per serving and is rich in healthy fats and protein.
Conclusion: Nourishing Your Brain for Better Mental Health
As we conclude our exploration of omega-3 fatty acids, it’s clear that these essential nutrients play a crucial role in maintaining mental health. To effectively manage anxiety and depression, focus on consuming 1-2 grams of EPA/DHA daily from sources like wild-caught salmon, walnuts, and chia seeds.
By making sustainable dietary changes and incorporating omega-3 rich foods, you can support both mental and physical health benefits. Remember, a balanced diet is just one aspect of a comprehensive approach to managing mental health.


[…] We will explore the top 10 teas known for their brain-boosting properties, discussing their biochemical effects and how they can be incorporated into your daily routine for improved concentration and overall brain health. […]
[…] staggering 32 distinct health risks – from heart disease to anxiety disorders – show direct ties to dietary choices, according to a 2024 BMJ review of 45 studies […]
[…] Spotting anxiety in early childhood requires careful observation. Behaviors like excessive clinginess, sleep disruptions, or sudden tantrums might signal deeper struggles. The CDC reports 7.1% of U.S. children have diagnosed anxiety disorders, but many cases remain undetected during critical developmental years. […]
[…] vegetables, legumes, and other foods contain non-heme iron, which accounts for the majority of people’s iron intake. As a vegan, […]
[…] your dietary choices can significantly influence your anxiety levels and overall mental wellbeing? Anxiety affects approximately 7.3% of the global population, manifesting as constant feelings of tension, […]
[…] EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid): Primarily found in fatty fish, EPA helps reduce inflammation and may improve symptoms of depression. […]
[…] practice can strengthen positive pathways. A Harvard study confirms this rewires emotions, reducing anxiety over […]
[…] keep us full longer? We test that idea with a fast, no-cook breakfast that uses fiber, protein, and omega-3s to nudge appetite control and support mindful […]
[…] such as B vitamins, zinc, and magnesium, are associated with an increased risk of depression and anxiety […]